Fractions: Mixed numbers
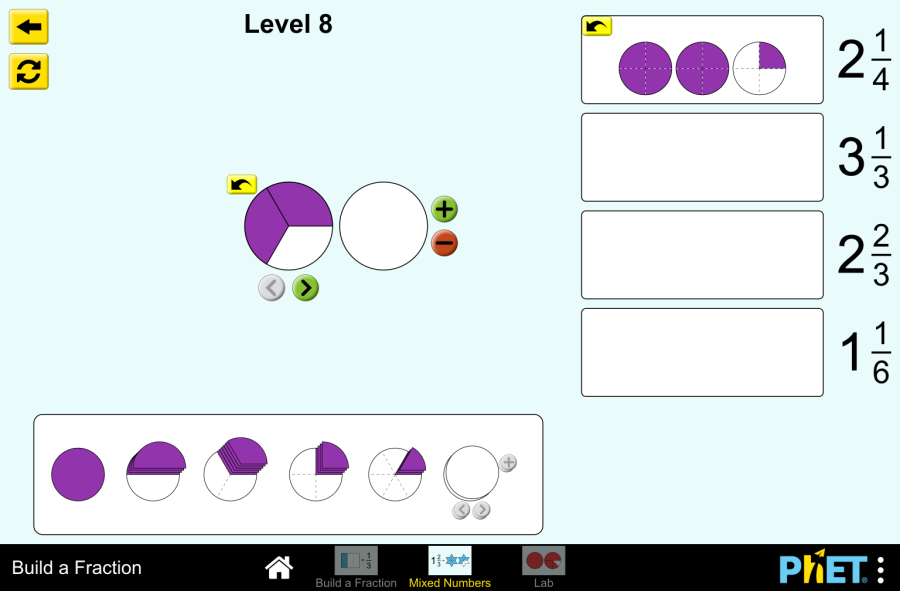
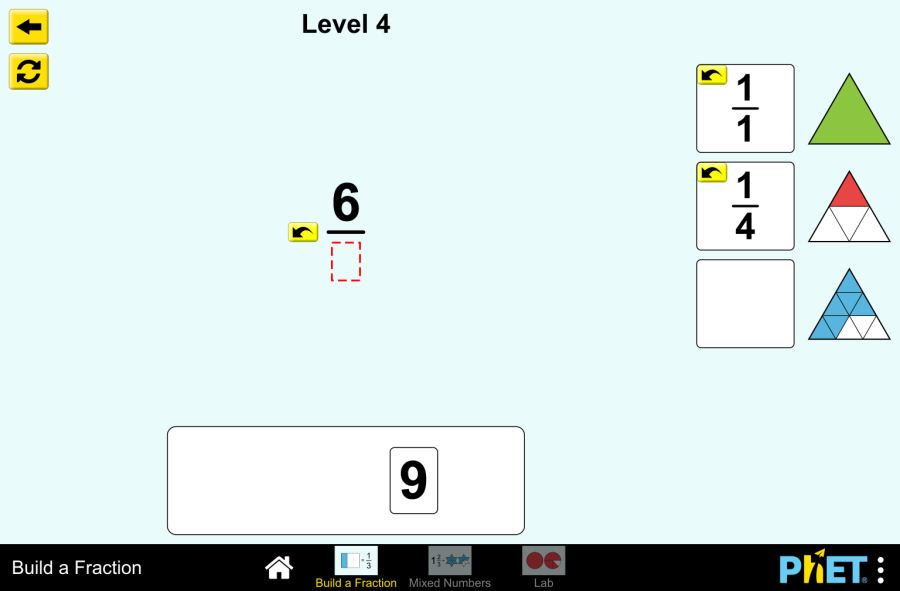
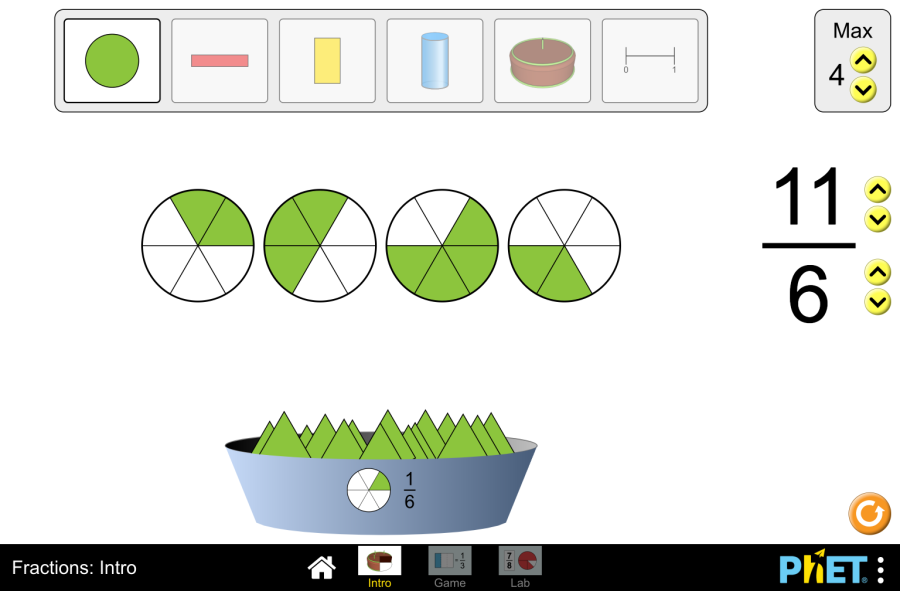
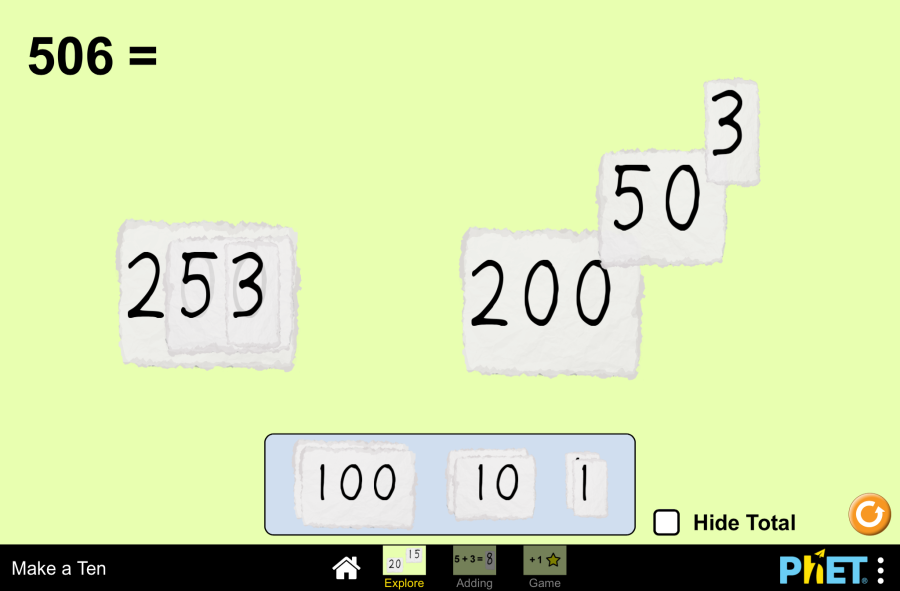
Objective: This virtual work is designed for use in mathematics lessons on the following topics Theoretical part What is a mixed number? Imagine a pizza cut into 8 equal slices. If you eat 3 whole pizzas and 5 more slices from the fourth pizza, how can you keep track of how many pizzas you have eaten? This is where mixed numbers come in. A mixed number has two parts: In our example with the pizza we ate, we’ll write it like this 3 5/8. This reads as “three whole five-eighths”. Example: Why do we use mixed numbers? How do you make an improper fraction into a mixed number? An improper fraction is a fraction where the numerator is greater than the denominator. For example, 11/4. To convert an improper fraction into a mixed number, you must So 11/4 = 2 3/4. Virtual Experiment The Fraction: Mixed Number Simulation allows students to explore and compare different representations of fractions, including mixed numbers. Allows flexibility to explore the correspondence between parts using numbers and representations. Progression: Part 1. Introduction Step 1. Start the simulation: You will be presented with 3 different modes: “Intro”, “Game” and “Lab”. Open the “Intro” section. Step 2. In the workspace you will be presented with: Step 3. Launch the mixed numbers button. Select the appearance of the fraction according to your needs. Step 4. Click the button that increases the amount of empty skeleton of the fraction model. You will have 2 skeletons. Step 5. Fill the first skeleton completely and the second skeleton halfway. You will have a mixed number. Step 6. Increase the size of the fraction. Create different mixed numbers by filling the skeletons. Step 7. Click the button that increases the number of empty skeletons of the fraction model and display some more empty skeletons. Step 8. Make mixed numbers by collecting and filling the skeletons with different fractions from the shapes. Part 2. Lab Section Step 9. Select the Lab section. You will be given shapes to assemble fractions. You can choose round or rectangular shapes. You are given a blank space to write the fraction and an empty skeleton. Below that are the numbers needed for the numerator and denominator of the fraction. Step 10. Construct a mixed number from the numbers. Step 11. Arrange the shapes on the empty skeleton according to the given fraction. You can add the necessary number of empty skeletons using the “Add” button. Step 12. You can create a copy in the workspace by dragging the empty space next to the numbers and the empty skeleton next to the shapes. Step 13. Try to collect some mixed fractions. Conclusion Virtual work can be a useful tool for students to become familiar with and understand the concept of mixed numbers. Creating mixed numbers with a visual representation makes it easier to learn the topic. Glossary of terms
Fractions: Mixed numbers Read More »